Because you typically need to pay vendors quickly, accounts payable is a current liability. You can take out loans to help expand your small business. A loan is considered a liability until you pay back the money you borrow to a bank or person.
- Business owners who keep a chart of accounts handy will have an advantage when it comes to accounting.
- Liabilities in accounting meaning show it as an obligation, which makes the companies legally bound to pay back as they do in case of a debt or for the services or the goods consumed or utilized.
- Basically, these are any debts or obligations you have that need to get paid within a year.
- The portion of the vehicle that you’ve already paid for is an asset.
- When this happens, you can reasonably estimate the amount of the resulting liability.
Types of liabilities in accounting

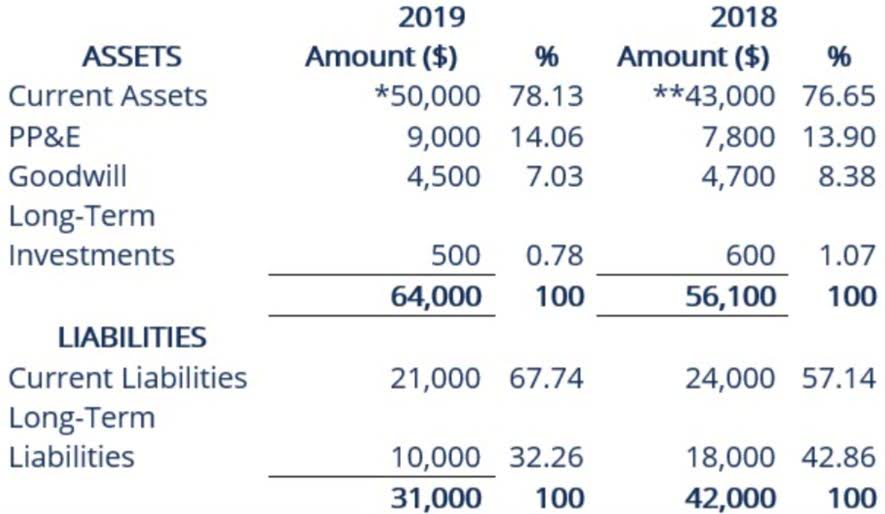
Current liabilities can include things like accounts payable, accrued expenses and unearned revenue. Long-term liabilities include areas such as bonds payable, notes payable and capital leases. Contingent liabilities are liability accounts list liabilities that could happen but aren’t guaranteed. Liabilities are carried at cost, not market value, like most assets.
Examples of Contingent Liabilities

This involves reconciling accounts, verifying outstanding obligations, and addressing any discrepancies promptly. Unlock the potential of liability account with the comprehensive Lark glossary guide. Explore essential accounting terms and relevant Lark solutions. A liability is anything how is sales tax calculated you owe to another individual or an entity such as a lender or tax authority. The term can also refer to a legal obligation or an action you’re obligated to take. It might signal weak financial stability if a company has had more expenses than revenues for the last three years because it’s been losing money for those years.
Accounting best practices on liability accounts
This is to help guarantee that any debts or obligations your business has can get met. A liability is an obligation payable by a business to either internal (e.g. owner) or an external party (e.g. lenders). There are mainly four types of liabilities in a business; current liabilities, non-current liabilities, contingent liabilities & capital. To create a COA for your own business, you will want to https://www.bookstime.com/ begin with the assets, labeling them with their own unique number, starting with a 1 and putting all entries in list form. The balance sheet accounts (asset, liability, and equity) come first, followed by the income statement accounts (revenue and expense accounts). Because most accounting these days is handled by software that automatically generates financial statements, rather than pen and paper, calculating your business’ liabilities is fairly straightforward.
Current liabilities
Liabilities are settled over time through the transfer of economic benefits including money, goods, or services. They’re recorded on the right side of the balance sheet and include loans, accounts payable, mortgages, deferred revenues, bonds, warranties, and accrued expenses. A liability account in accounting represents the various financial obligations a company owes to others, recorded on its balance sheet.

Any money that you owe would get considered as a liability. And it would stay as a liability until the invoice gets paid off. The liabilities that your business has are going to fluctuate. And if you have more debt, then you’re going to have higher liabilities. Making sure that you’re paying off your debts regularly will help reduce your overall business liabilities.
